TABLE OF CONTENTS
Every business owner should have a firm idea of their business model. That might sound obvious, but you’d be surprised by just how many budding entrepreneurs forge ahead into business without actually understanding how their operation will work.
A business model is basically the ‘core structure’ of how an organisation creates, delivers, and captures value. It doesn’t matter whether you’re a new startup exploring innovative business models, or an established company that wants to refine an existing business model – developing the right business plan could be your key to success.
What is a business model?
In simple terms, a business model breaks down the specifics of how a business generates income and creates value for its customers. In a perfect world, it should outline how your company will make money from various products or services.
The term ‘business model’ has changed over the last few decades, especially as industries have been transformed by technology and digital business models. New business models like the freemium business model or subscription-based models, for example, are very common in the software and media industries.
Bottom line: a competitive business model should explain how you will differentiate yourself in the market.
Key components of a company’s business model
To fully understand a business model, it can be helpful to break it down into its main building blocks. The ‘business model canvas’ is a popular tool that some businesses use to better understand their own model. Here are some of the primary elements you’ll want to incorporate into your own business model concept:
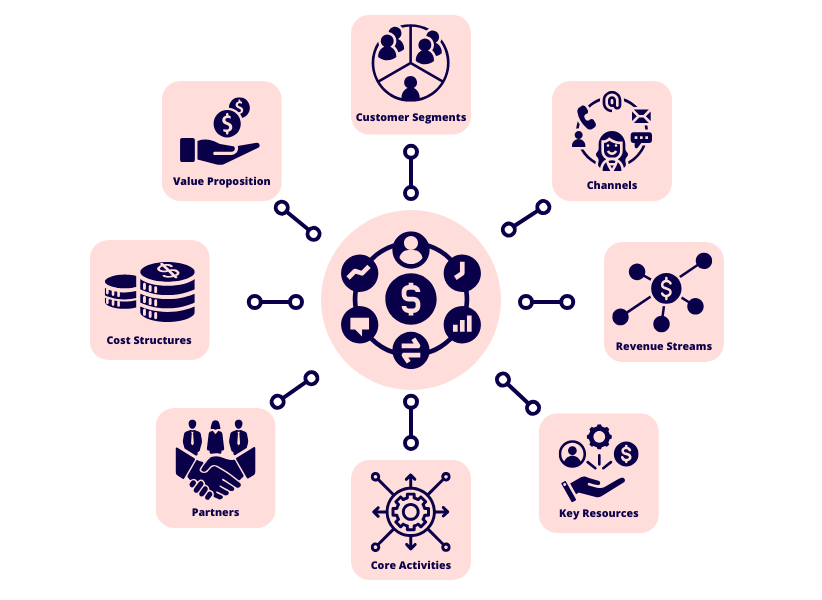
Value proposition
This describes what unique benefit your business gives its customers. It answers the question: “Why would a customer choose us over a competitor?” The answer could be that it’s a low-cost solution, a specialised service, a high-quality product, etc. Think about low-cost airlines that have budget-friendly flights – that’s their primary value proposition. This is also quite often tied to your brand identity.
Customer segments
Customer segments are the specific groups of people or organisations your business wants to serve. Identifying these target markets will help you tweak your products and services to meet customers’ needs. Some businesses focus on a single customer segment, while others might need to target multiple segments.
Channels
Channels refer to the ways you deliver your products or services to customers (e.g. online platforms, retail stores, third-party distributors). Businesses relying on an e-commerce model, for example, will use digital channels as their main way of reaching customers, while traditional business models for retail operations will rely on physical stores.
Customer relationships
How do you interact with and retain your customers? This part of your business model describes the strategies and approaches your company uses to build and maintain customer loyalty. Social media platforms and CRM (customer relationship management) tools are really handy ways to support your customers over the long term.
Revenue streams
This is all about how your business makes money from each customer segment. Different business models can generate revenue in different ways, including direct sales, subscription-based models that require ongoing payments, or a freemium model that gives away a basic service for free with the hopes of converting customers to a premium paid option.
Key resources
These are the essential assets needed to successfully operate your business model. Depending on your industry and business type, this might include raw materials, intellectual property or even human capital (i.e. skilled employees). Think about a software company that relies on talented developers as its key resource, or a manufacturing company that needs to acquire specific raw materials.
Core activities
These are the most important tasks or actions your business needs to perform in order to operate well and deliver value to customers. Some key activities could involve manufacturing, software development, marketing or customer service, depending on your business type.
Partners
Key partners will include things like your suppliers, distributors and other businesses you collaborate with to make your business model work. Building partnerships can be a great way to reduce costs or bring in resources that might not be available internally.
Cost structure
This final section should identify all the expenses that are involved in running your business. Fixed costs like rent and salaries are front-and-centre, but there might also be variable costs that fluctuate based on your production volume. Having a good grasp of your cost structure will help in setting a sustainable cost model and managing your resources as effectively as possible.
Different types of business models
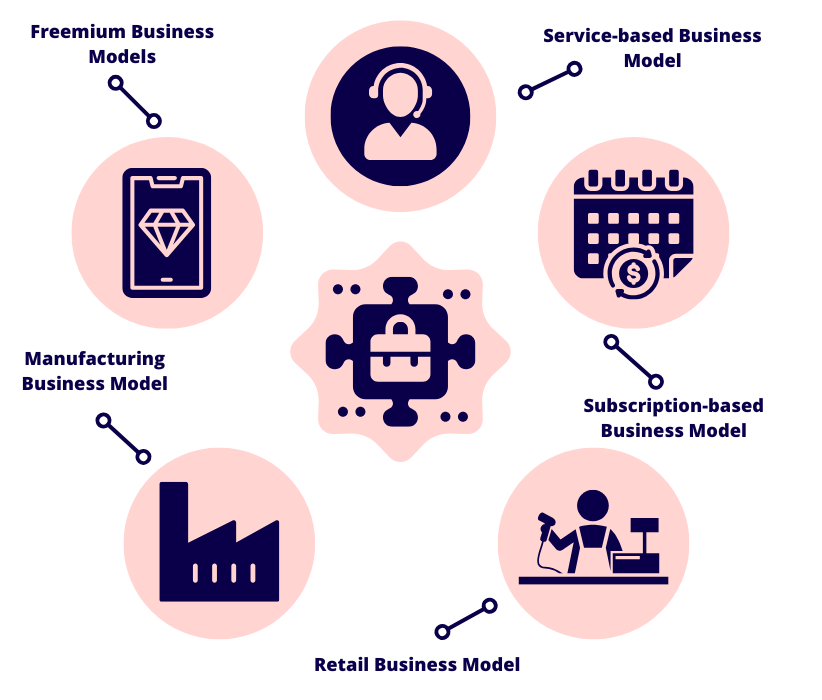
Service-based business model
In this model, businesses deliver services to customers in exchange for a fee. It’s extremely popular in industries like consulting, healthcare, accounting and legal services. Achieving success with a service-based model is often dependent on whether you can build strong client relationships and provide a high level of expertise.
Subscription-based business model
Subscription models revolve around giving customers access to a product or service on a recurring basis (e.g. monthly or annually). It’s really popular among software service providers and streaming platforms, and it’s a way to generate consistent revenue through ongoing payments.
Retail business model
This model is based on selling products directly to consumers. Retailers can choose to do this through physical stores, online platforms or a combination of both. The retail model is highly competitive, so your company will need to have to capacity to maintain inventory levels and respond to changing customer preferences.
Manufacturing business model
In the manufacturing model, a company makes goods and sells them to wholesalers, retailers or directly to consumers. It’s a model that relies on you having a lot of capital investment, as well as strong supply chain management and the ability to produce your products at scale.
Freemium business models
In the freemium model, a company ‘sells’ a basic product or service for free and charges for premium features or upgrades. You’ll see this model used by software companies, especially with apps and online services, as it can be used to attract a large user base.
How to choose the right business model
Still unsure which business model best applies to your company? That’s okay – it’s a big decision that will have an impact on your overall strategy and growth potential. Here are some of the most important things to consider when choosing a model for your business:
- Target market: Who are your customers and what do they value?
- Competitive advantage: What sets your business apart from competitors?
- Cost structure: Can your revenue model support the costs of running the business?
- Revenue potential: How will your preferred model generate income sustainably?
Choosing and creating a successful business model is something every business owners needs to tackle, whether you’re running a startup or an established enterprise. It’s the best way to clearly define how your company will deliver value, generate revenue and – perhaps most important of all – stay competitive.